Pipeline detail
FM503(Treatment for autoimmune disease)
| Classification | Description |
|---|---|
| FM503 |
|
| Indication |
|
| Unmet Needs |
|
| Mechanism of Action |
|
| Efficacy |
|
| Market |
|
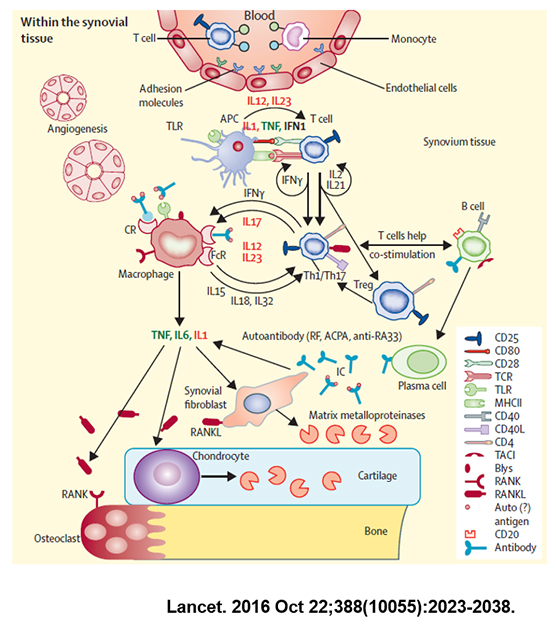
Rheumatoid arthritis is a disease caused by inflammation of the tissue that surrounds the joint called the synovium. The disorder can occur in any movable joint that has a synovial membrane. It is a chronic disease that progresses over months to years.
The exact cause of rheumatoid arthritis is unknown. However, thanks to advances in modern medicine, partial progress has been made. It is presumed that when a person genetically predisposed to rheumatoid arthritis receives some external stimulus, the body's immune system attacks the body abnormally and causes inflammation. In other words, rheumatoid arthritis is a type of autoimmune disease in which the body's immune system, which should play a defense against external bad bacteria, attacks its own body tissues.
Drugs for rheumatoid arthritis include primary drugs such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and steroids and secondary drugs that suppress rheumatoid arthritis itself by affecting the body's immune system.
However, despite the existence of such an effective treatment, there are patients with rheumatoid arthritis recurrence and unresponsiveness, and safety issues for infection are being raised, so the demand for drug development with a new mechanism is high.
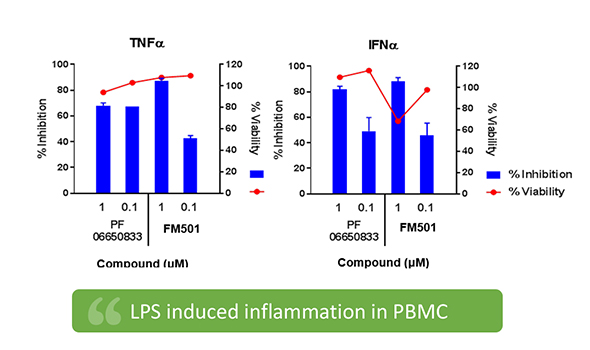
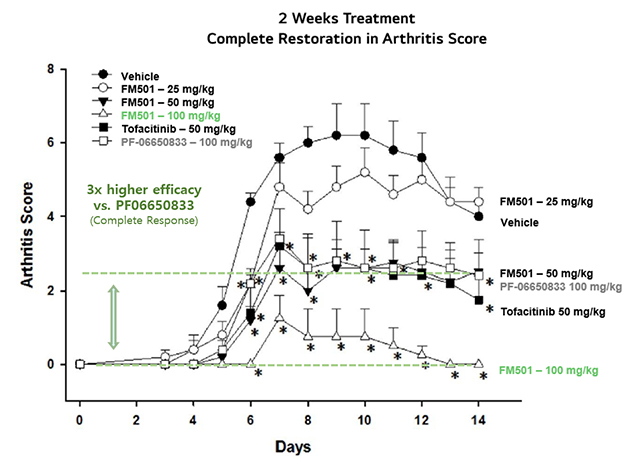
- FM501 is an autoimmune drug that inhibits IRAK4 and shows a high anti-inflammatory effect by suppressing inflammatory activity through the TLR pathway.
- FM501 confirmed the excellent anti-inflammatory and non-clinical treatment effects compared to Pfizer's same target clinical candidate.
- In addition, its oral availability has high expectations of competitive advantage in terms of convenience compared to previously approved injections.
- Superior anti-inflammatory effect to the competitor (PF-66650833_Pfizer)
- Orally available autoimmune treatment
- Novel pharmacological action differentiated from currently approved treatment (IRAK4 vs. TNF-α, IFN, and JAK)


Superior anti-inflammatory effect to competitor


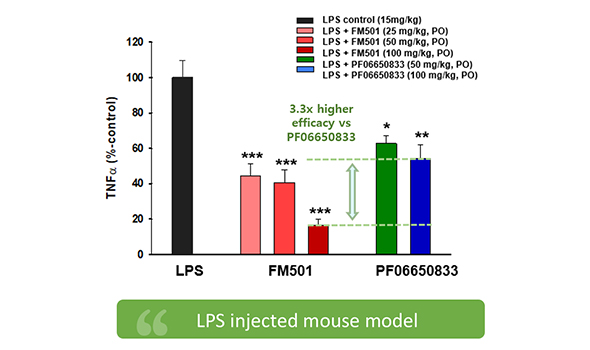


Excellent therapeutic effect differentiated from competitors in the rheumatoid arthritis mouse (CAIA) model


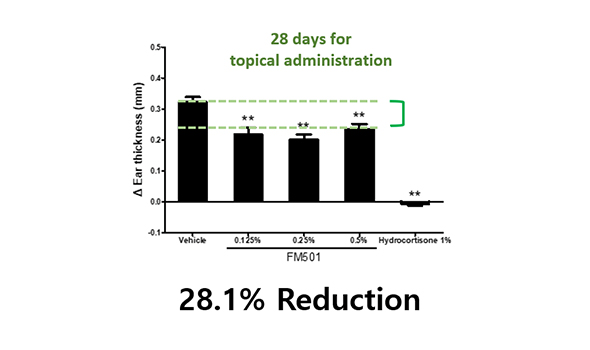
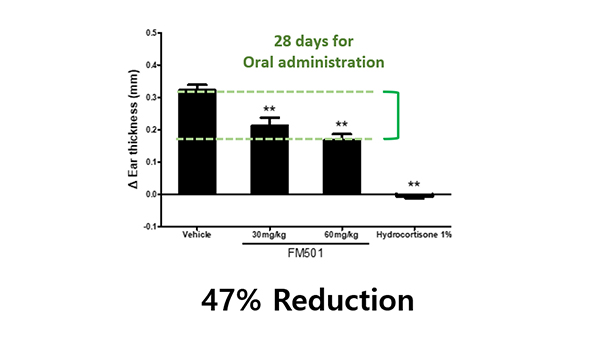
Orally treated mice showed better efficacy than mice treated topical administration in atopic dermatitis mouse model




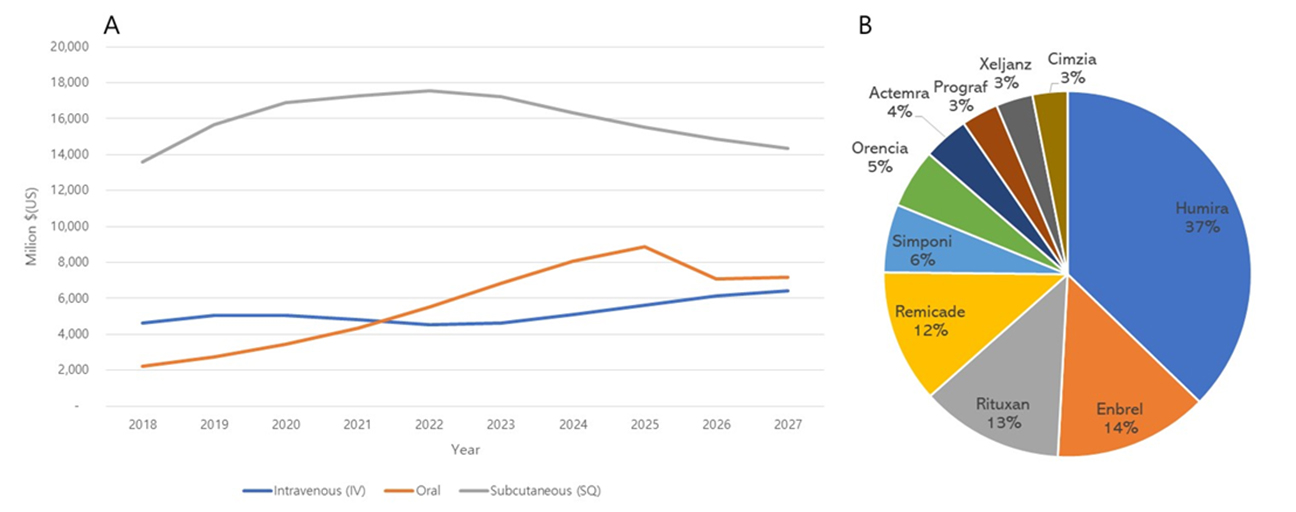
- According to Datamonitor Healthcare, the rheumatoid arthritis market (USA, Japan, France, Germany, Italy, Spain, UK) will grow from US$ 20.4 billion in 2018 to US$ 27.9 billion by 2027. It is expected to increase by about $7.5 billion, growing at a CAGR of 3.55%.
- The market share of rheumatoid arthritis treatment was 37% for Humira, followed by Enbrel at 14%, Rituxan at 13%, Remicade at 12%, and others at 24%. In the case of formulations, injections are expected to dominate from 2018 to 2027, but oral formulations such as Xeljanz (Pfizer) and Prograf (Astellas) account for 10.8% (2018). is expected to rise to 25.6% (by 2027).